| Group | Anatolian (with Hittite, Lydian etc.), Early Anatolian (with Hittite and Palaic) |
| Geography | Luwian was spoken in south-eastern Anatolia. After the Hittite Kingdom was defeated, they migrated south to Syria and at the same time part of Luwians moved to the west, to lands later known as Lycia. |
| History | First Luwian documents refer to the 16th century B.C. Luwian was used together with Hittite in the capital city of Hattusa, many Luwian documents were found in Royal libraries there. In the 13th century Luwian influenced greatly the official Hittite language of the Empire, and it must have been the result of great power of Luwians in the capital. But still, mainly Luwian language was spoken not in Hatti, the central province of the Empire, but in the country called Arzawa, west of Hatti, and in Cilicia, south of Hatti. There were also Luwian speakers in the East of the country. The culmination of Luwian language development took place in the 13 - 12th centuries B.C., when most of inscriptions were written. After that it began to retreat constantly under the pressure of Aramaeans and Assyrians who invaded Hittite lands from the South and East. And finally, in the 11th century Luwian sources disappear in the West, in the 7th century B.C. in the East Hatti Luwian was assimilated by Aramaic. |
| Phonetics | There are some slight differences in phonetics between Luwian and Hittite: Luwian lost middle vowels [e] and [e.] turning them into [a] and [i] respectively, and since then had just three vowels. The Common Anatolian consonant *k became a spirant; the Indo-European *gh completely disappeared (IE *ghesr- 'hand' > Luwian issari-). |
| Nominal Morphology | A peculiar accusative form for 'animate' neuter nouns appeared in Luwian. Another peculiarity is that the genitive case markers disappear, replaced by adjectival postfixes. |
| Verbal Morphology | In the structure of the verb, the same opposition of two types of conjugation (-mi and -hi) as in Hittite is also seen, but not so clearly. The latter type of conjugation was understood in Luwian as the set of past tense endings. A strange feature of Luwian was its verbs at the beginning of the sentences. |
| Lexicon | The vocabulary of Luwian contains much of Indo-European, but also a lot of terms borrowed from the Hurritic language, especially in the religious sphere. |
| Writing | Luwian Hieroglyphs, Cuneiform |
| Close Contacts | Contacted long with Hurritic and Hatti languages, later influenced by Aramaic. |
| Sample | a-ri-ja-ad-da-li-iš DIM-an-za šar-ri ka-ši-i hu-e-hu-i-ja tap-pa-aš-ša-it
šar-ri ti-ja-mi hu-i-hu-i-ja.
Friendly God of thunder, from above to the ground come, from the sky downwards to the ground come. |
| Picture | 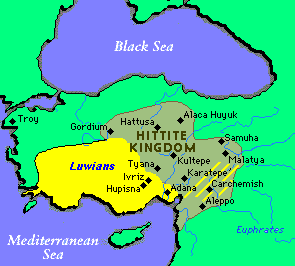 |
| More info |